One step preparation of ZnFe2O4/Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2 nanocomposite with improved As(V) removal capacity
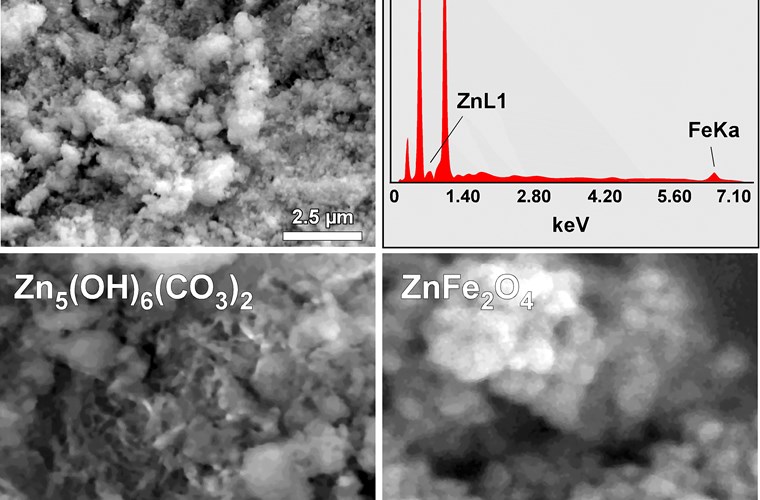
High magnification SEM images obtained in ICMAB/CSIC facilities provided a better view of the morphological characteristics of a ZnFe2O4/Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2 nanocomposite.
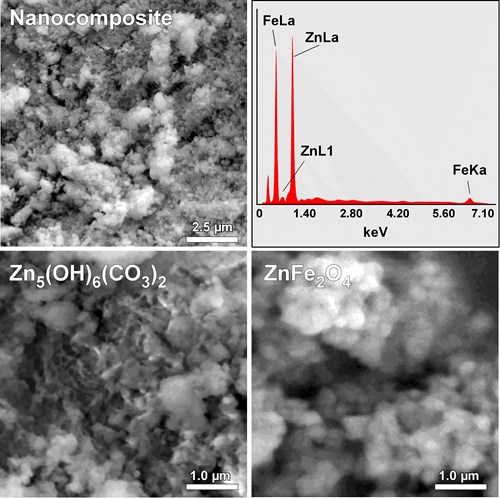
SEM image of the ZnFe2O4/Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2 nanocomposite (Zn/Fe=2.5) and corresponding EDX elemental analysis spectrum. Regions rich in Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2 sheets and ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles.
The paper introduces a novel nanocomposite consisting of a zinc ferrite and a layered zinc hydroxyl-carbonate (hydrozincite) for the improved adsorption of arsenic at concentrations complying with the drinking water regulation limits.
The main advance of the adsorbent is the high capacity against As(V) which overcomes reported values for both commercially available and laboratory-developed iron oxy-hydroxides. Such performance is attributed to the added capacity provided by the ion-exchange between carbonate ions from the material’s structure and arsenate oxy-ions.
Synthesis optimization indicates that the best adsorbent is obtained when the percentage of hydrozincite reaches 74 %wt.
The development of the studied adsorbent is considered as direct solution for high arsenic adsorption efficiencies in a wider pH range. Furthermore, it opens new perspectives to the design of materials which utilize their whole volume, rather than only their surface, in the adsorption of pollutants from drinking water.
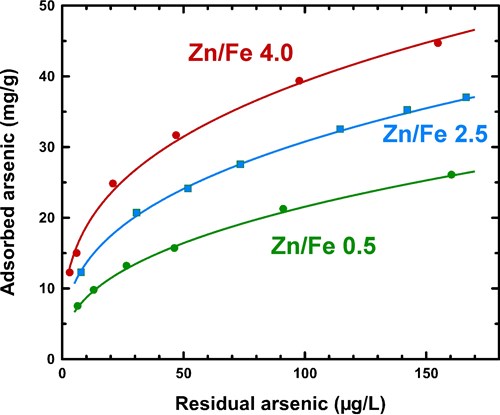
Adsorption isotherms of Zn/Fe nanocomposites with different metal ratio at pH 7 using natural-like water spiked with As(V). Continuous line indicates the Freundlich fitting.
NFFA-EUROPE FACILITIES AND TECHNIQUES
The Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images were obtained using a Quanta 200 ESEM FEG FEI microscope with a field-emission gun operating at 30 kV @ CSIC-ICMAB in Barcelona
The NFFA-Europe proposal under which this research has been carried out also included access to SQUID and Magneto-transport @ CSIC-ICMAB in Barcelona
PUBLICATION DETAILS
December 14th, 2017 - Separation Science and Technology
One step preparation of ZnFe2O4/Zn5(OH)6(CO3)2 nanocomposite with improved As(V) removal capacity
S. Tresintsia, E. Kokkinosa, A. Kamoub, K. Simeonidisa, M. Mitrakasa, G. Kyriakoua, A. Zouboulisc
a Department of Chemical Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. b Department of Physics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. c Department of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
Reference: DOI :10.1080/01496395.2017.1413390
For more information: Dr. Konstantinos Simeonidis, ksime@physics.auth.gr

